The analysis of the reinforced concrete section performed by spColumn conforms to the provisions of the Strength Design Method and Unified Design Provisions with all conditions of strength satisfying the applicable conditions of equilibrium and strain compatibility.
In most building design calculations, such as the examples shown for flat plate or flat slab concrete floor systems, all building columns may be subjected to biaxial bending (Mx and My) due to lateral forces and unbalanced moments from both directions of analysis. This requires an evaluation of the column P-Mx-My interaction diagram in two directions simultaneously (axial force interaction with biaxial bending).
This example shows the calculations needed to obtain one point on the three-dimensional failure surface (biaxial Mx-My interaction diagram). Generating the three-dimensional failure surface (interaction diagram) for a column section subjected to a combined axial force and biaxial bending moments is tedious and challenging for engineers and the use of a computer aid can save time and eliminate errors. StructurePoint’s spColumn program can, quickly, simply and accurately generate the three-dimensional failure surface (interaction diagram) for all commonly encountered column, beam or wall sections in addition to highly complex and irregular cross-sections.
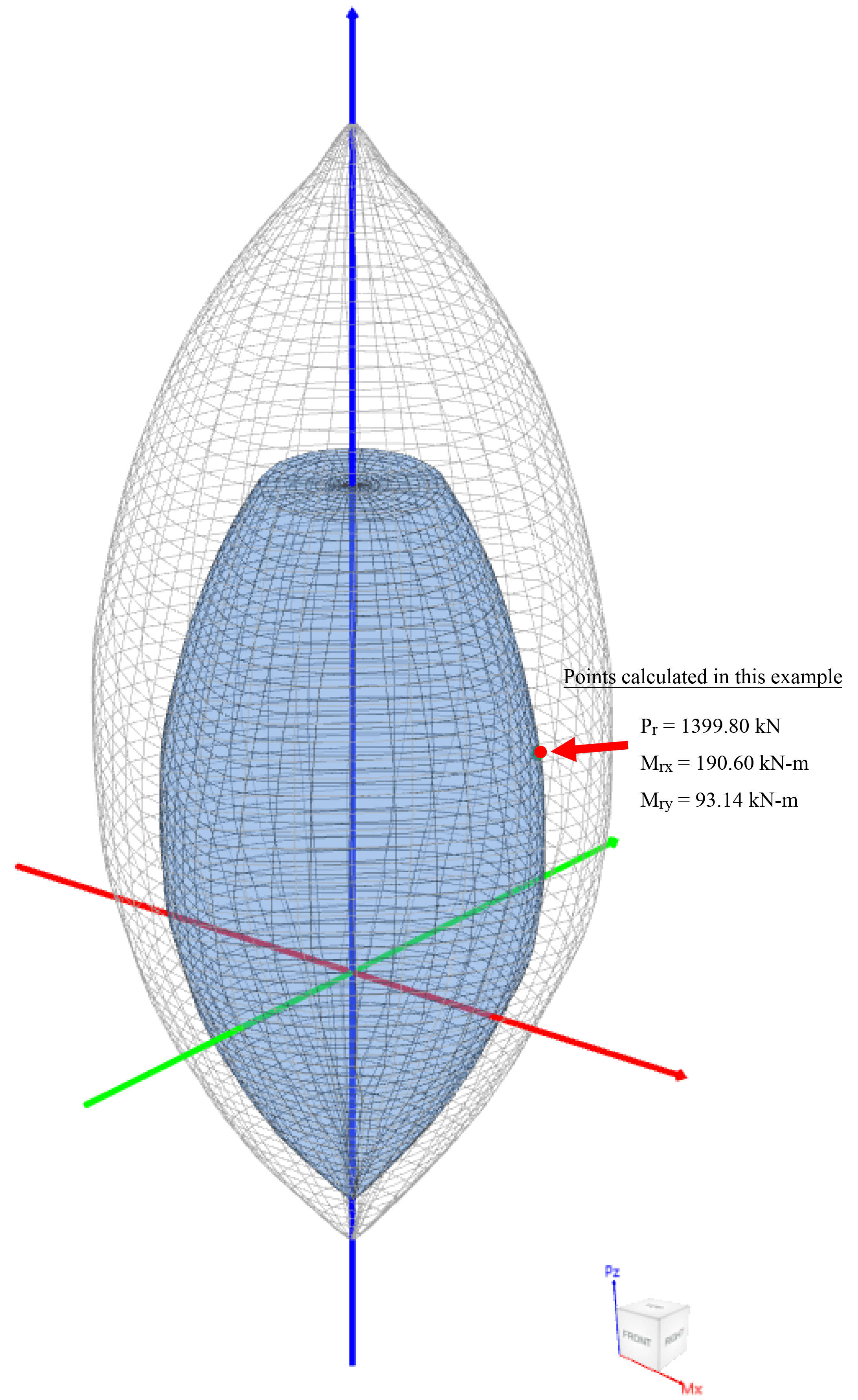
Figure 10 - Interaction Diagram in Two Directions (Biaxial) (spColumn)
The spColumn “Diagrams” module is a powerful tool especially for investigating interaction diagrams (failure surfaces) for columns and walls sections subjected to a combined axial force and biaxial bending moments. The module allows the user to view and analyze 2D interaction diagrams and contours along with 3D failure surfaces in a multi viewport environment. The following figure shows three views of:
1. P-M interaction diagram cut at angle of 26º
2. Mx-My interaction diagram cut at axial load of 1399.80 kN in compression
3. A 3D failure surface (interaction diagram) showing the points calculated in this example.
Figures 12, and 13 show 3D visualization of failure surface with a horizontal and vertical plane cut, respectively.
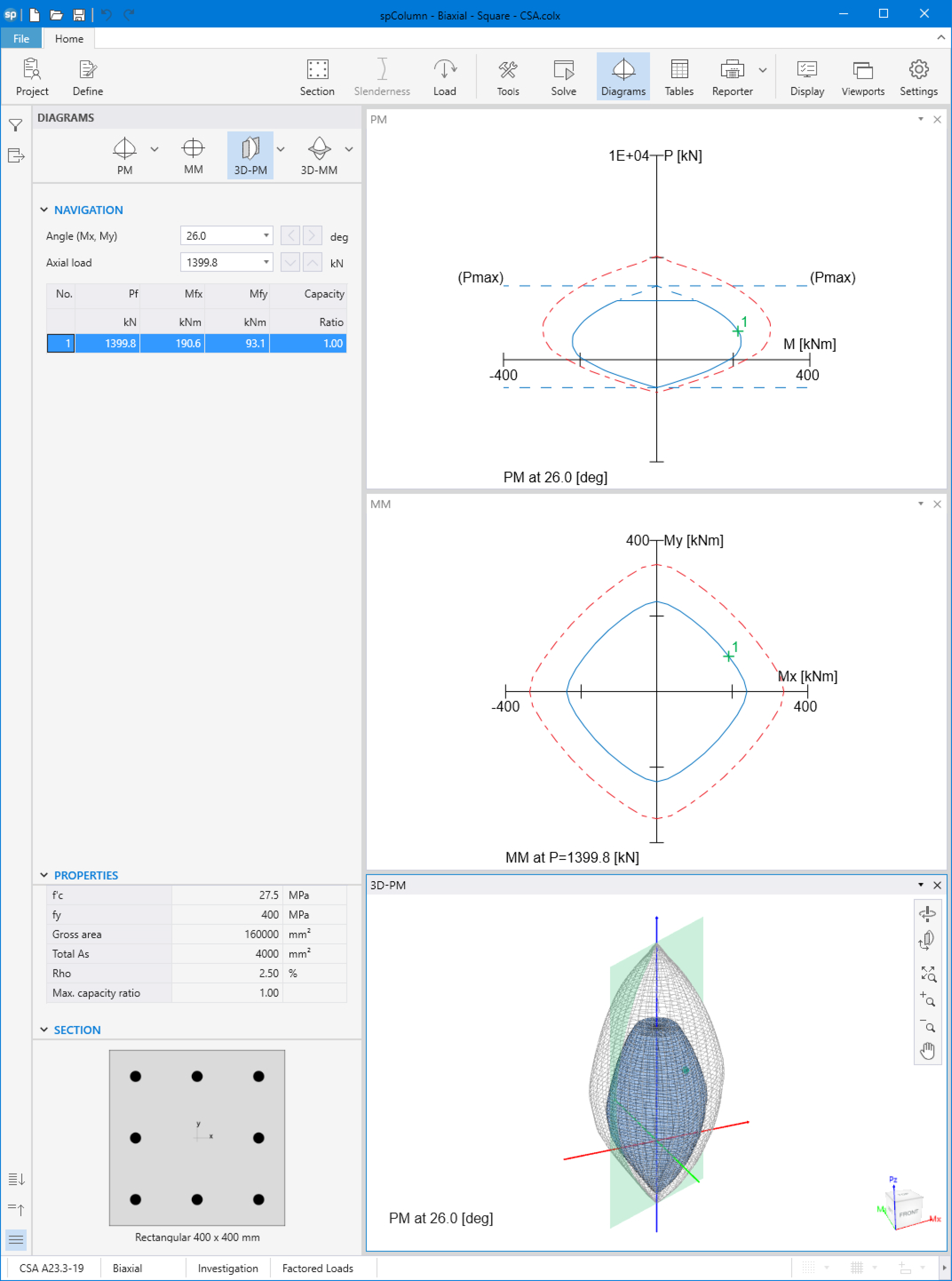
Figure 11 - Diagrams Module (spColumn)
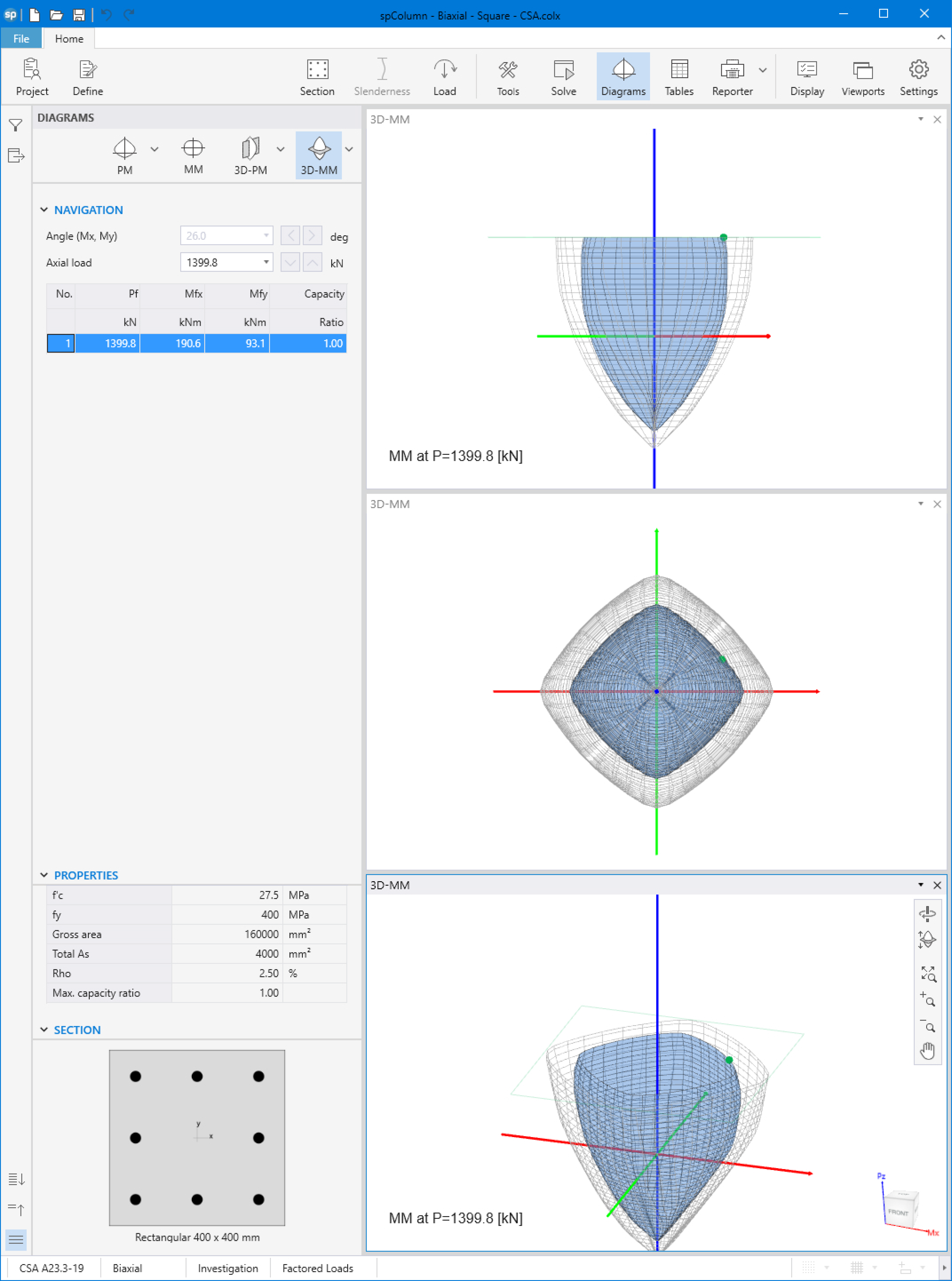
Figure 12 - 3D Visualization of Failure Surface with a Horizontal Plane Cut a P = 1399.80 kN (spColumn)
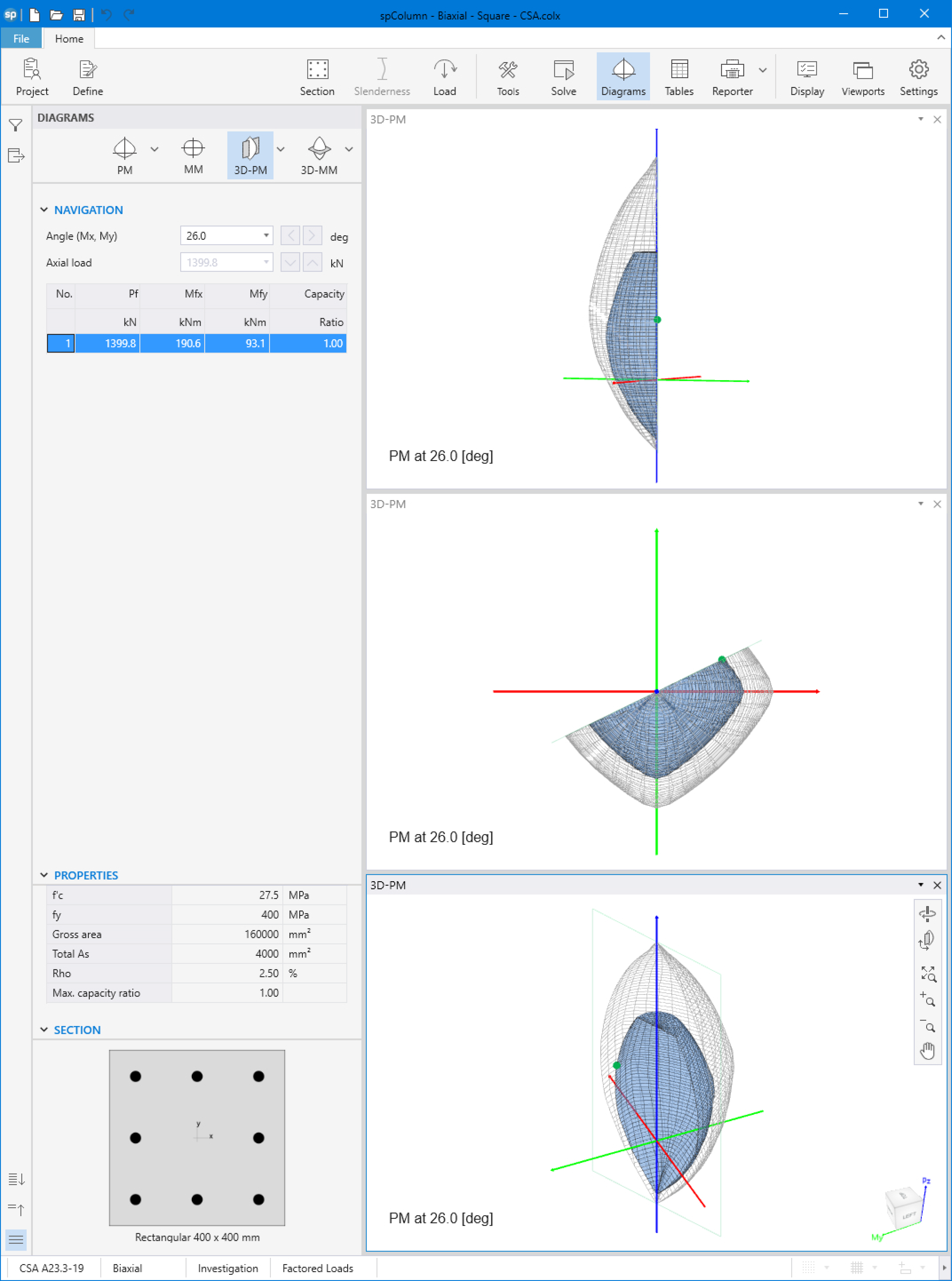
Figure 13 - 3D Visualization of Failure Surface with a Vertical Plane Cut at 26º (spColumn)