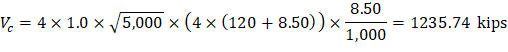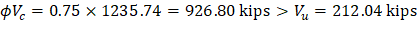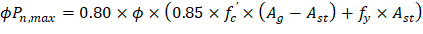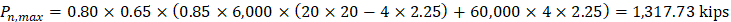1.1. For Flat Plate (Without Drop Panels)
1.1.1. Slab Minimum Thickness - Deflection
ACI 318-14 (Table 8.3.1.1) |
In lieu of detailed calculation for deflections, ACI 318 Code gives minimum slab thickness for two-way construction without interior beams in Table 8.3.1.1.
For this flat plate slab systems the minimum slab thicknesses per ACI 318-14 are:
Exterior Panels: | ACI 318-14 (Table 8.3.1.1) |
But not less than 5 in. | ACI 318-14 (8.3.1.1(a)) |
Interior Panels: | ACI 318-14 (Table 8.3.1.1) |
But not less than 5 in. | ACI 318-14 (8.3.1.1(a)) |
Where ln = length of clear span in the long direction = 30 × 12 – 20 = 340 in.
Try 11 in. slab for all panels (self-weight = 150 pcf × 11 in. /12 = 137.5 psf)
1.1.2. Slab Shear Strength - One Way Shear
At a preliminary check level, the use of average effective depth would be sufficient. However, after determining the final depth of the slab, the exact effective depth will be used in flexural, shear and deflection calculations. Evaluate the average effective depth (Figure 2):
| |
| |
|
Where:
cclear = 3/4 in. for # 6 steel bar | ACI 318-14 (Table 20.6.1.3.1) |
db = 0.75 in. for # 6 steel bar |
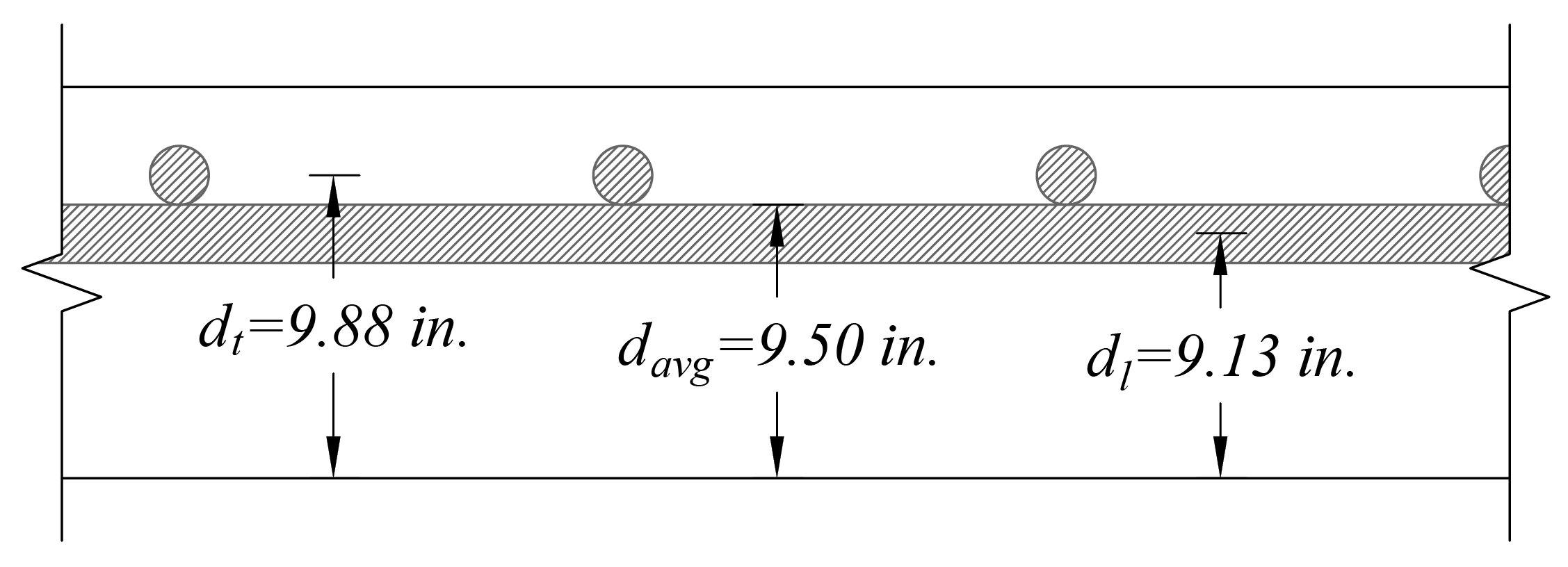
Figure 2 – Average Effective Depth for Flat Plate
Factored dead load, | ||
Factored live load, | ACI 318-14 (5.3.1) | |
Total factored load, |
Check the adequacy of slab thickness for beam action (one-way shear) | ACI 318-14 (22.5) |
At an interior column:
Consider a 12-in. wide strip. The critical section for one-way shear is located at a distance d, from the face of support (see Figure 3).
Tributary area for one-way shear is:
| |
| |
| ACI 318-14 (Eq. 22.5.5.1) |
where λ = 1 for normal weight concrete, more information can be found in “Concrete Type Classification Based on Unit Density” technical article.
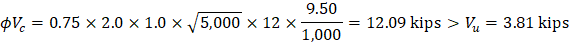
Slab thickness of 11 in. is adequate for one-way shear.
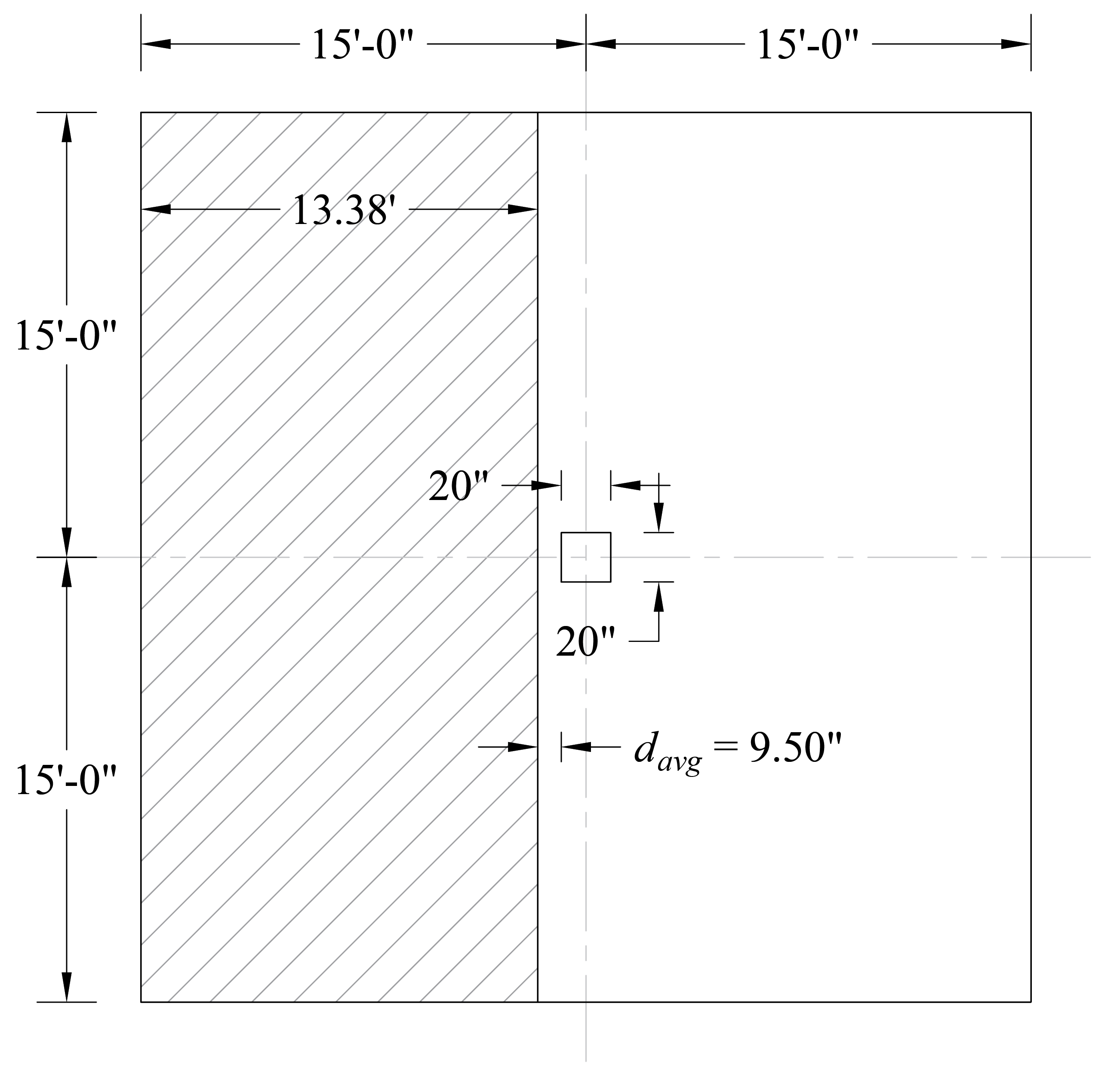
Figure 3 – Critical Section for One-Way Shear
1.1.3. Slab Shear Strength - Two-Way Shear
Check the adequacy of slab thickness for punching shear (two-way shear) at an interior column (Figure 4):
Tributary area for two-way shear is:
| |
| |
| ACI 318-14 (Table 22.6.5.2(a)) |
| |
|
Slab thickness of 11 in. is not adequate for two-way shear. It is good to mention that the factored shear (Vu) used in the preliminary check does not include the effect of the unbalanced moment at supports. Including this effect will lead to an increase of Vu value as shown later in section 4.2.
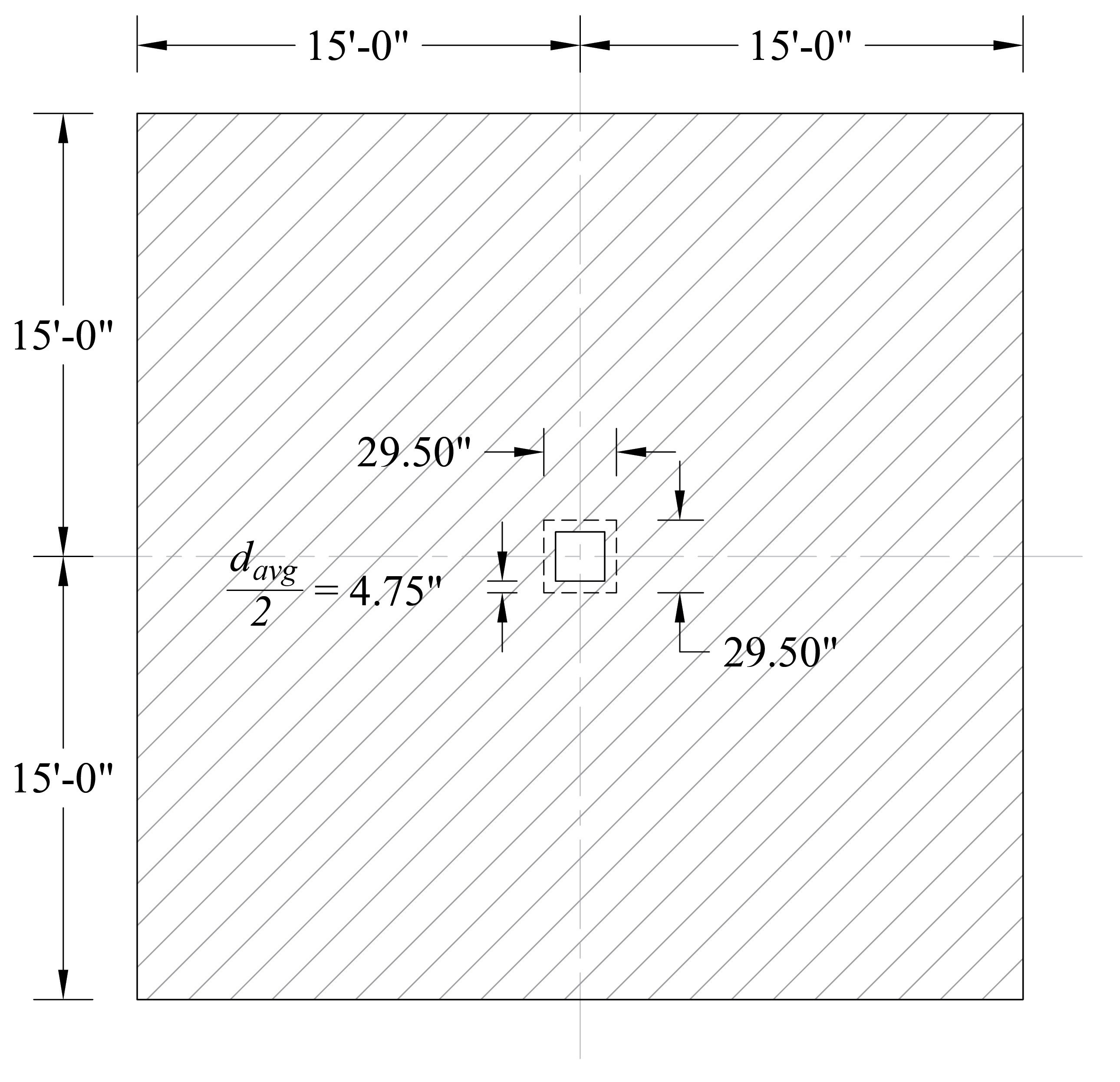
Figure 4 – Critical Section for Two-Way Shear
In this case, four options could be used: 1) to increase the slab thickness, 2) to increase columns cross sectional dimensions or cut the spacing between columns (reducing span lengths), however, this option is assumed to be not permissible in this example due to architectural limitations, 3) to use headed shear reinforcement, or 4) to use drop panels. In this example, the latter option will be used to achieve better understanding for the design of two-way slab with drop panels often called flat slab.
Check the drop panel dimensional limitations as follows:
1) The drop panel shall project below the slab at least one-fourth of the adjacent slab thickness. ACI 318-14 (8.2.4(a))
Since the slab thickness (hs) is 10 in. (see page 9), the thickness of the drop panel should be at least:
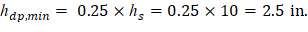
Drop panel dimensions are also controlled by formwork considerations. The following Figure shows the standard lumber dimensions that are used when forming drop panels. Using other depths will unnecessarily increase formwork costs.
For nominal lumber size (2x), hdp = 4.25 in. > hdp, min = 2.5 in.
The total thickness including the slab and the drop panel (h) = hs + hdp = 10 + 4.25 = 14.25 in.
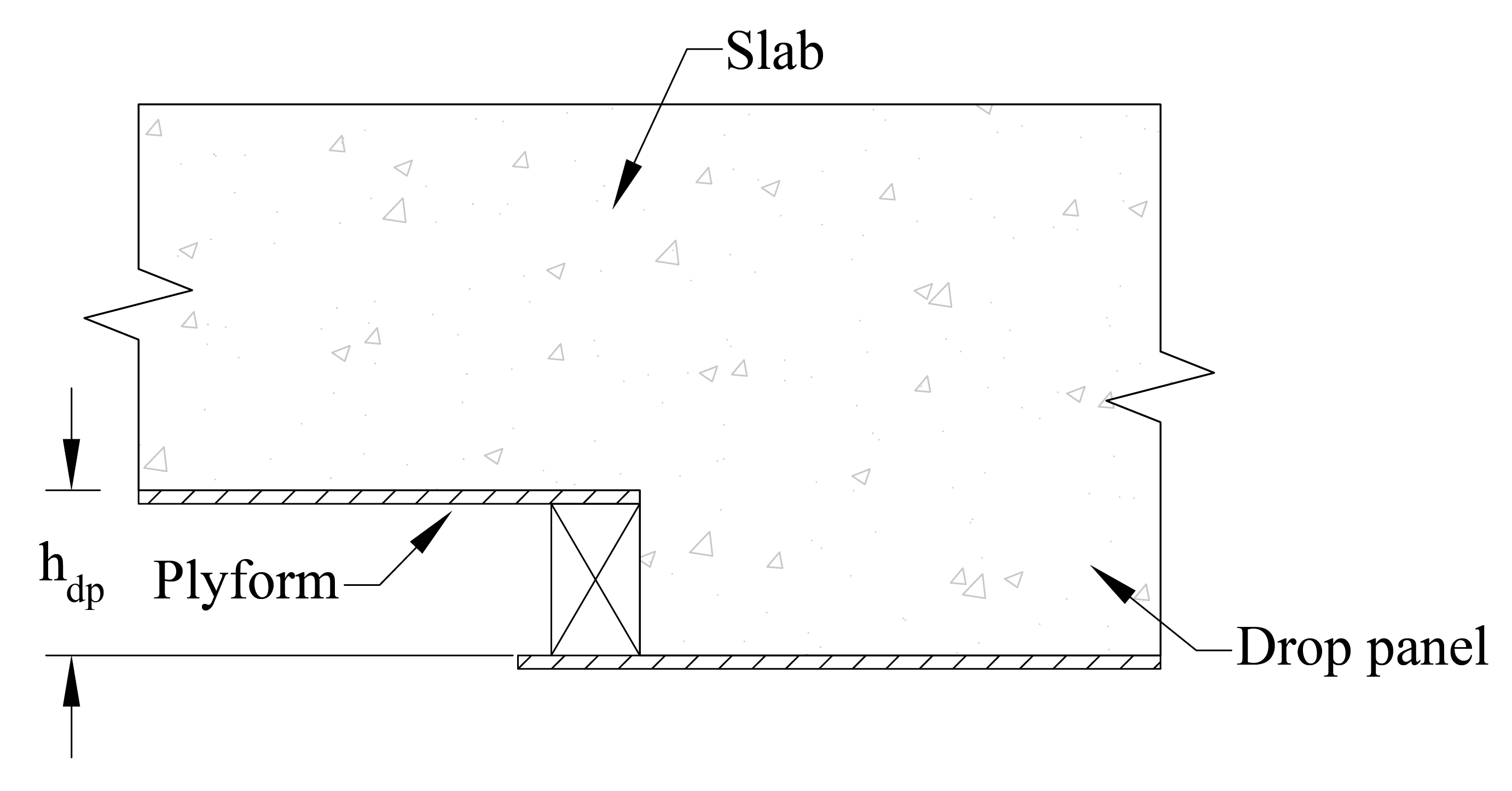
Nominal Lumber Size (in.) | Actual Lumber Size (in.) | Plyform Thickness (in.) | hdp (in.) |
2x | 1 1/2 | 3/4 | 2 1/4 |
4x | 3 1/2 | 3/4 | 4 1/4 |
6x | 5 1/2 | 3/4 | 6 1/4 |
8x | 7 1/4 | 3/4 | 8 |
Figure 5 – Drop Panel Formwork Details
2) The drop panel shall extend in each direction from the centerline of support a distance not less than one-sixth the span length measured from center-to-center of supports in that direction. | ACI 318-14 (8.2.4(b)) |
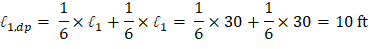
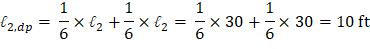
Based on the previous discussion, Figure 6 shows the dimensions of the selected drop panels around interior, edge (exterior), and corner columns.
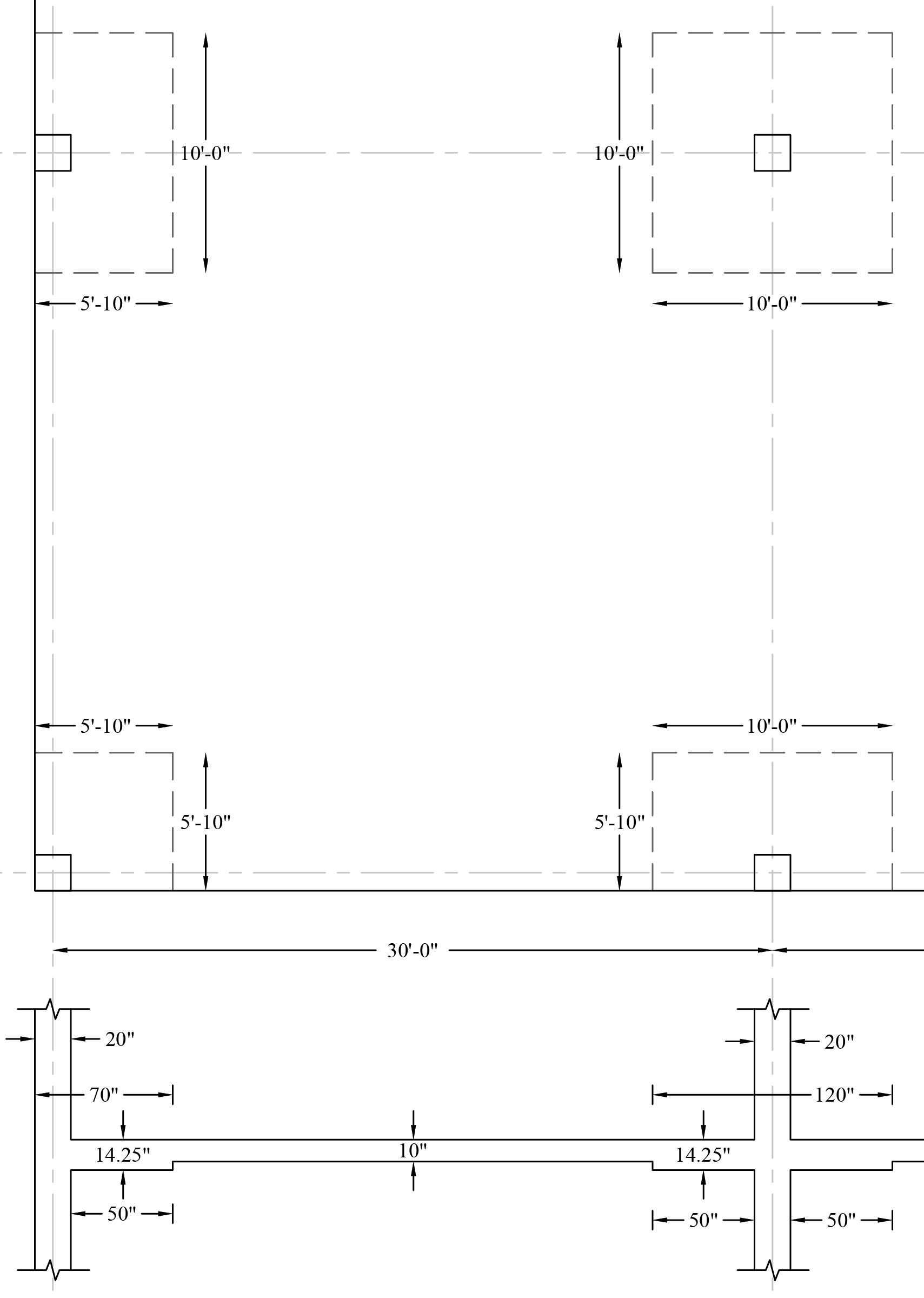
Figure 6 – Drop Panels Dimensions
1.2. For Flat Plate (with Drop Panels)
For slabs with changes in thickness and subjected to bending in two directions, it is necessary to check shear at multiple sections as defined in the ACI 318-14. The critical sections shall be located with respect to:
1) Edges or corners of columns. ACI 318-14 (22.6.4.1(a)) 2) Changes in slab thickness, such as edges of drop panels. ACI 318-14 (22.6.4.1(b))
1.2.1. Slab Minimum Thickness - Deflection
ACI 318-14 (Table 8.3.1.1) |
In lieu of detailed calculation for deflections, ACI 318 Code gives minimum slab thickness for two-way construction without interior beams in Table 8.3.1.1.
For this flat plate slab systems the minimum slab thicknesses per ACI 318-14 are:
Exterior Panels: | ACI 318-14 (Table 8.3.1.1) |
But not less than 4 in. | ACI 318-14 (8.3.1.1(b)) |
Interior Panels: | ACI 318-14 (Table 8.3.1.1) |
But not less than 4 in. | ACI 318-14 (8.3.1.1(b)) |
Where ln = length of clear span in the long direction = 30 × 12 – 20 = 340 in.
Try 10 in. slab for all panels
Self-weight for slab section without drop panel = 150 pcf × 10 in. /12 = 125.00 psf
Self-weight for slab section with drop panel = 150 pcf × 14.25 in. /12 = 178.13 psf
1.2.2. Slab Shear Strength - One Way Shear
For critical section at distance d from the edge of the column (slab section with drop panel):
Evaluate the average effective depth:
| |
| |
|
Where:
cclear = 3/4 in. for # 6 steel bar | ACI 318-14 (Table 20.6.1.3.1) |
db = 0.75 in. for # 6 steel bar |
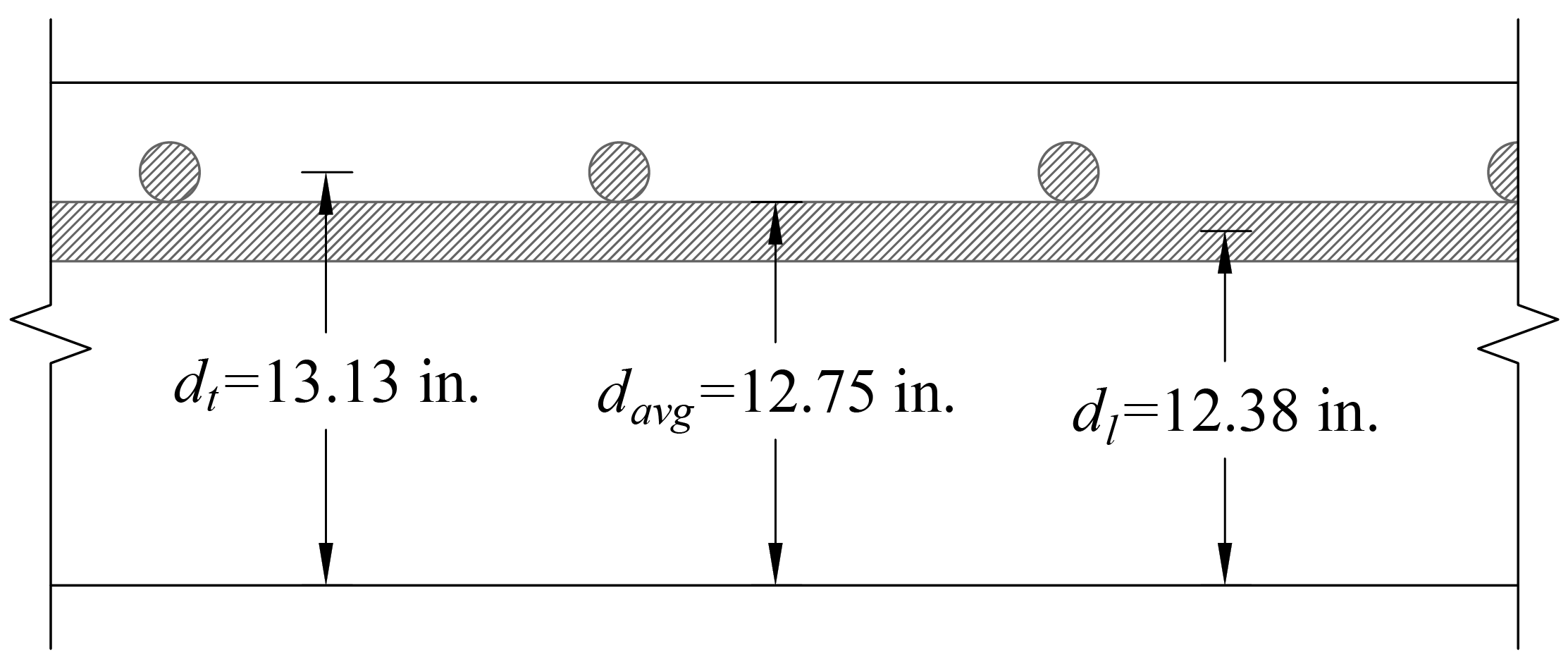
Figure 7 – Average Effective Depth for Slab Section with Drop Panel
Factored dead load, | ||
Factored live load, | ACI 318-14 (5.3.1) | |
Total factored load, |
Check the adequacy of slab thickness for beam action (one-way shear) from the edge of the interior column | ACI 318-14 (22.5) |
Consider a 12-in. wide strip. The critical section for one-way shear is located at a distance d, from the edge of the column (see Figure 8).
Tributary area for one-way shear is:
| |
| |
| ACI 318-14 (Eq. 22.5.5.1) |
where λ = 1 for normal weight concrete
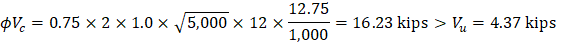
Slab thickness of 14.25 in. is adequate for one-way shear for the first critical section (from the edge of the column).
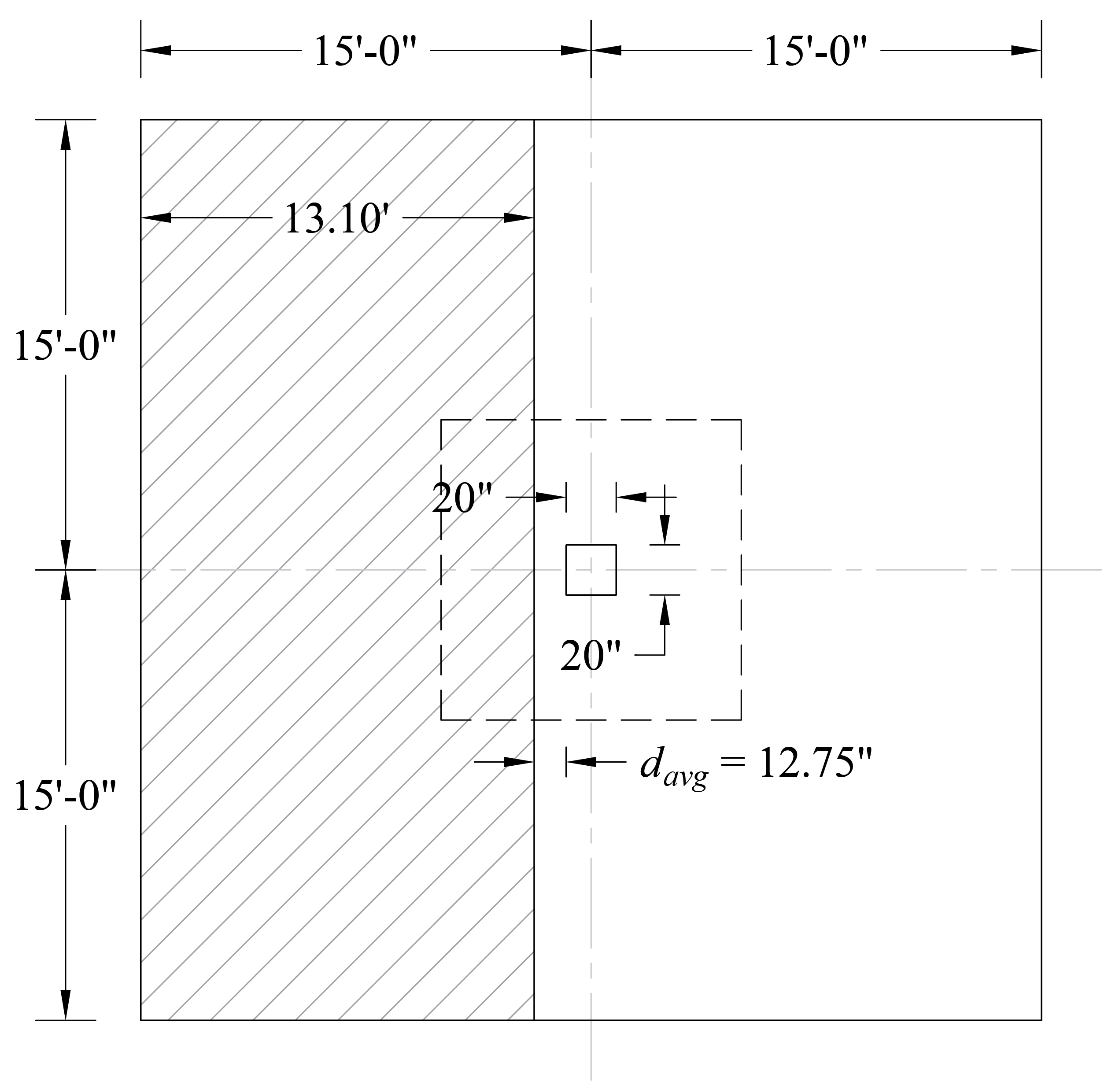
Figure 8 – Critical Section at Distance d from the Edge of the Column for One-Way Shear
For critical section at the edge of the drop panel (slab section without drop panel):
Evaluate the average effective depth:
| |
| |
|
Where:
cclear = 3/4 in. for # 6 steel bar | ACI 318-14 (Table 20.6.1.3.1) |
db = 0.75 in. for # 6 steel bar |
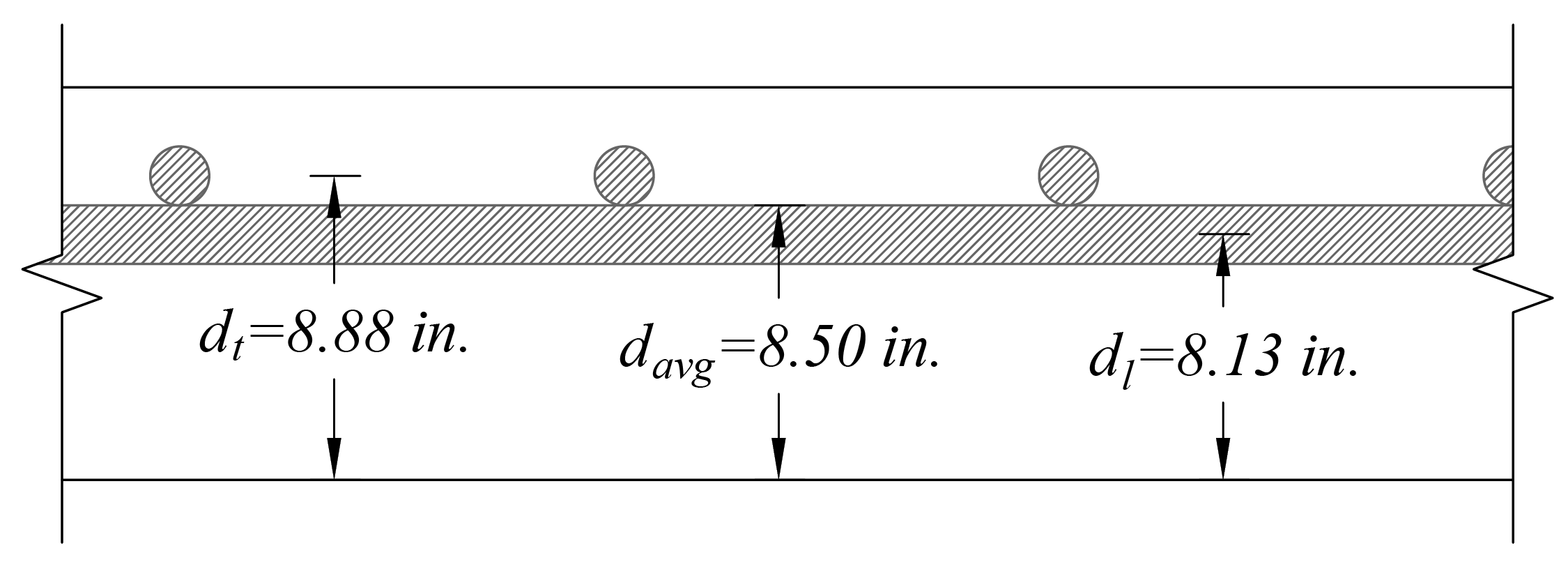
Figure 9 – Average Effective Depth for Slab Section without Drop Panel
Factored dead load, | ||
Factored live load, | ACI 318-14 (5.3.1) | |
Total factored load, |
|
Check the adequacy of slab thickness for beam action (one-way shear) from the edge of the interior drop panel | ACI 318-14 (22.5) |
Check the adequacy of slab thickness for beam action (one-way shear) from the edge of the interior drop panel (see Figure 10).
Tributary area for one-way shear is:
| |
| |
| ACI 318-14 (Eq. 22.5.5.1) |
where λ = 1 for normal weight concrete
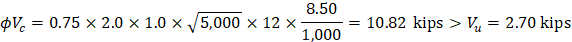
Slab thickness of 10 in. is adequate for one-way shear for the second critical section (from the edge of the drop panel).
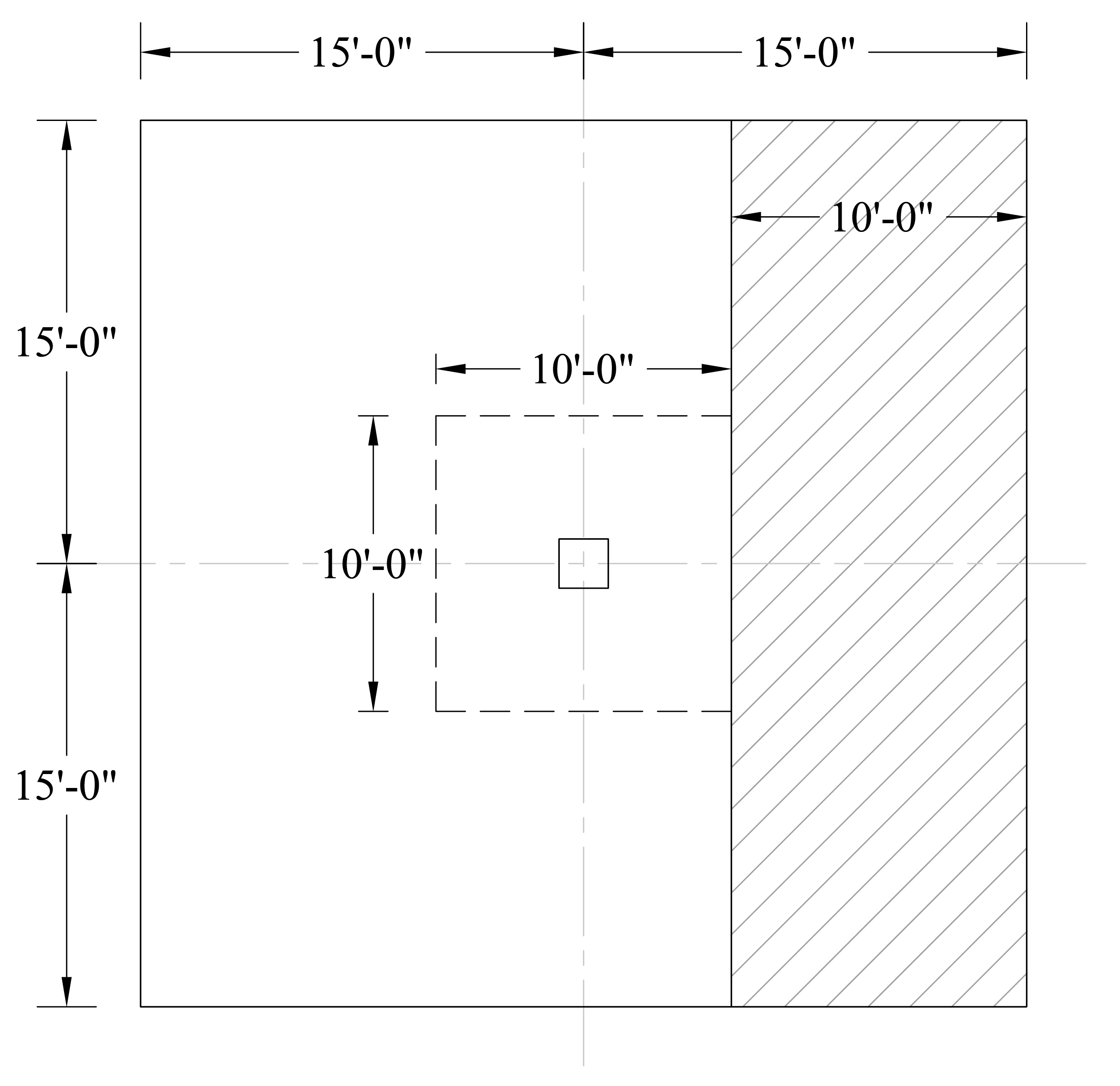
Figure 10 – Critical Section at the Face of the Drop Panel for One-Way Shear
1.2.3. Slab Shear Strength - Two-Way Shear
For critical section at distance d/2 from the edge of the column (slab section with drop panel):
Check the adequacy of slab thickness for punching shear (two-way shear) at an interior column (Figure 11):
Tributary area for two-way shear is:
ACI 318-14 (Table 22.6.5.2(a))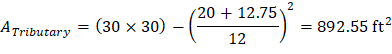
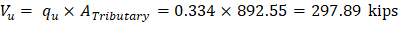
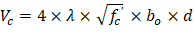 (For square interior column)
(For square interior column)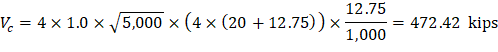
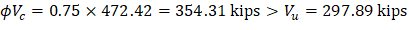
Slab thickness of 14.25 in. is adequate for two-way shear for the first critical section (from the edge of the column).
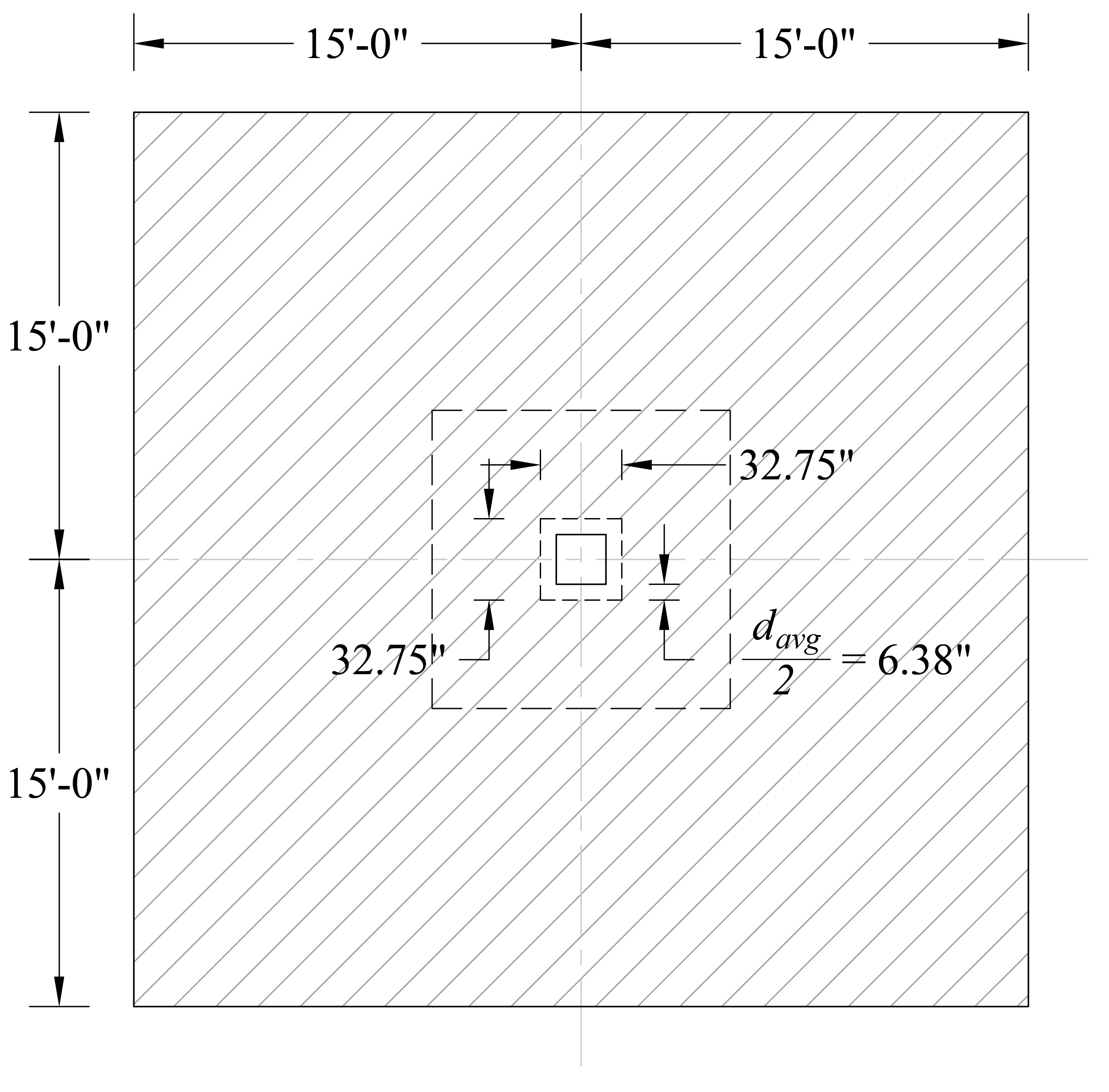
Figure 11 – Critical Section at d/2 from the Edge of the Column for Two-Way Shear
For critical section at the edge of the drop panel (slab section without drop panel):
Check the adequacy of slab thickness for punching shear (two-way shear) at an interior drop panel (Figure 12):
Tributary area for two-way shear is:
| |
| |
| ACI 318-14 (Table 22.6.5.2(a)) |
| |
|
Slab thickness of 10 in. is adequate for two-way shear for the second critical section (from the edge of the drop panel).
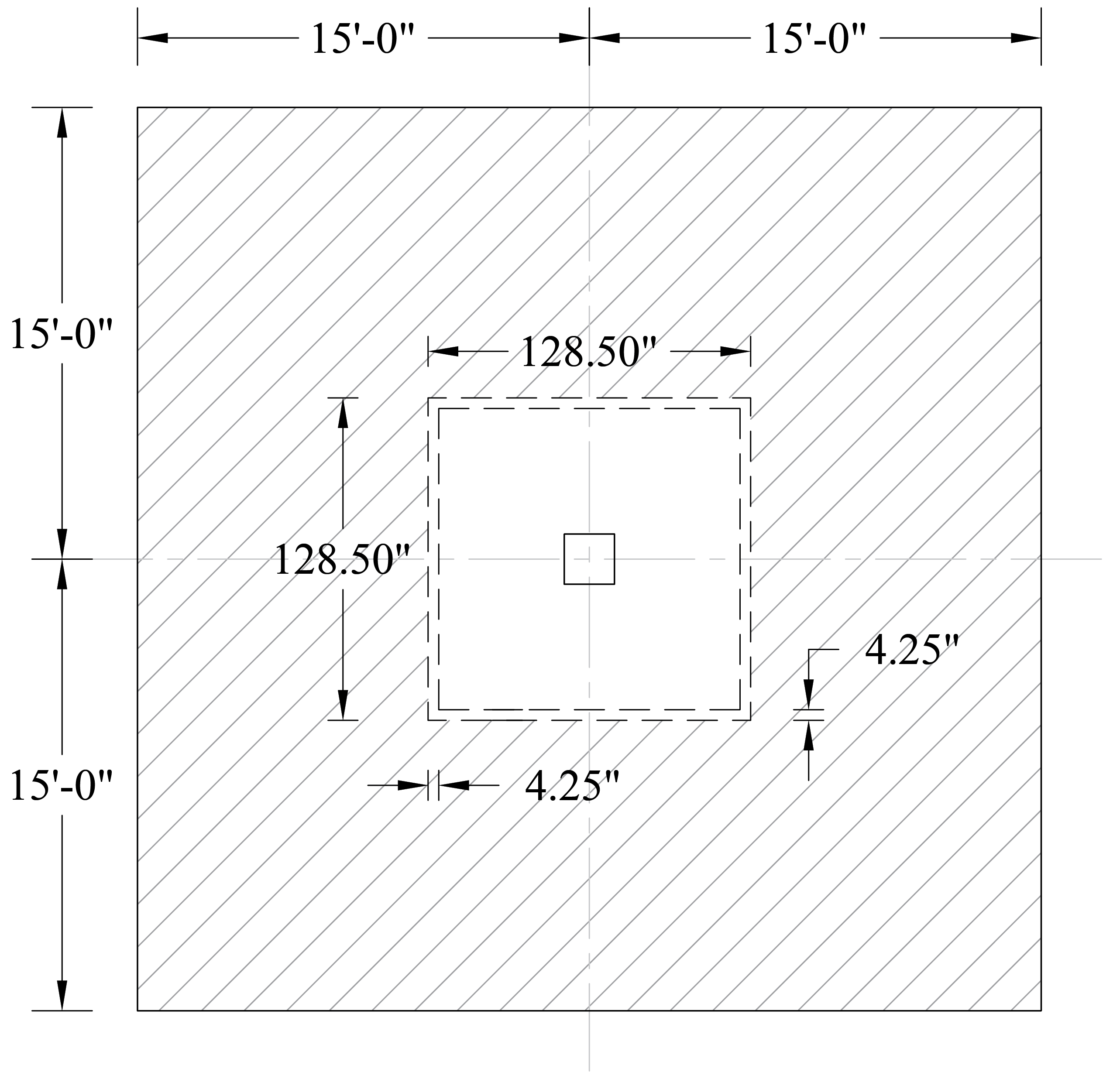
Figure 12 – Critical Section at d/2 from the Edge of the Drop Panel for Two-Way Shear
1.2.4. Column Dimensions - Axial Load
Check the adequacy of column dimensions for axial load:
For live load, superimposed dead load, and self-weight of the slab around an interior column:
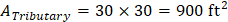
For self-weight of additional slab thickness due to the presence of the drop panel around an interior column:
qu = 333.75 – 270 = 63.75 psf (see page 10 and page 12)
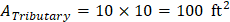
Assuming five story building
Assume 20 in. square column with 4 – No. 14 vertical bars with design axial strength, ϕPn,max of
| ACI 318-14 (22.4.2) |
| |
|
Column dimensions of 20 in. × 20 in. are adequate for axial load.
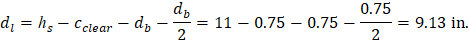
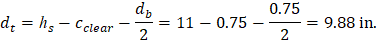
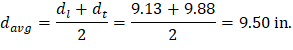
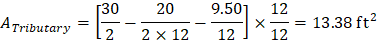
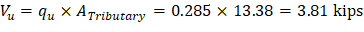
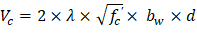
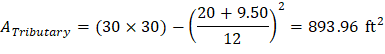
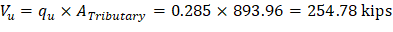
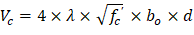 (For square interior column)
(For square interior column)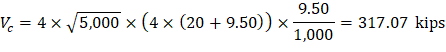
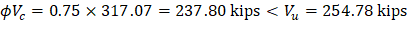
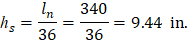
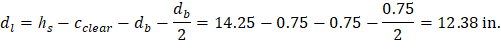
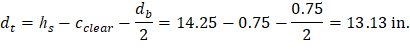
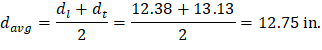
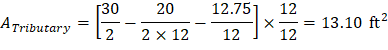
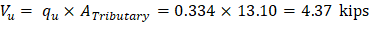
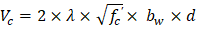
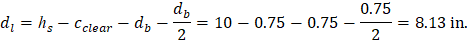
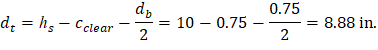
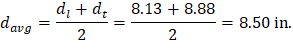
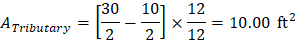
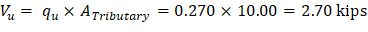
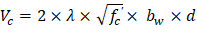
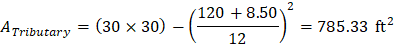
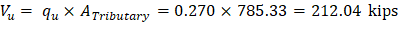
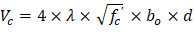 (For square interior column)
(For square interior column)